Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: Main Functions
The prefrontal lobes represent key elements for the modulation and control of human behavior. They are undoubtedly fundamental in the integration of cognitive, motivational and emotional information. Their connection to almost every region of the brain gives them great importance, and that is why studies and research about them are so important. Within the prefrontal lobes is the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: an area whose functions are vitally important to human behavior.
The frontal regions allow us to be autonomous beings, which gives us much of the control we have over our life. All this through the so-called executive functions, the functions that characterize us as human beings. Through these functions, we build our identity and develop self-awareness.
In this way, internal dialogue and communication with others are possible. Social cognition takes place in these regions, and from there emerges empathy, the ability to put yourself in the other’s shoes. At the same time, they also allow us to predict the behavior of others – by anticipating their intentions – or to understand aspects such as deception.
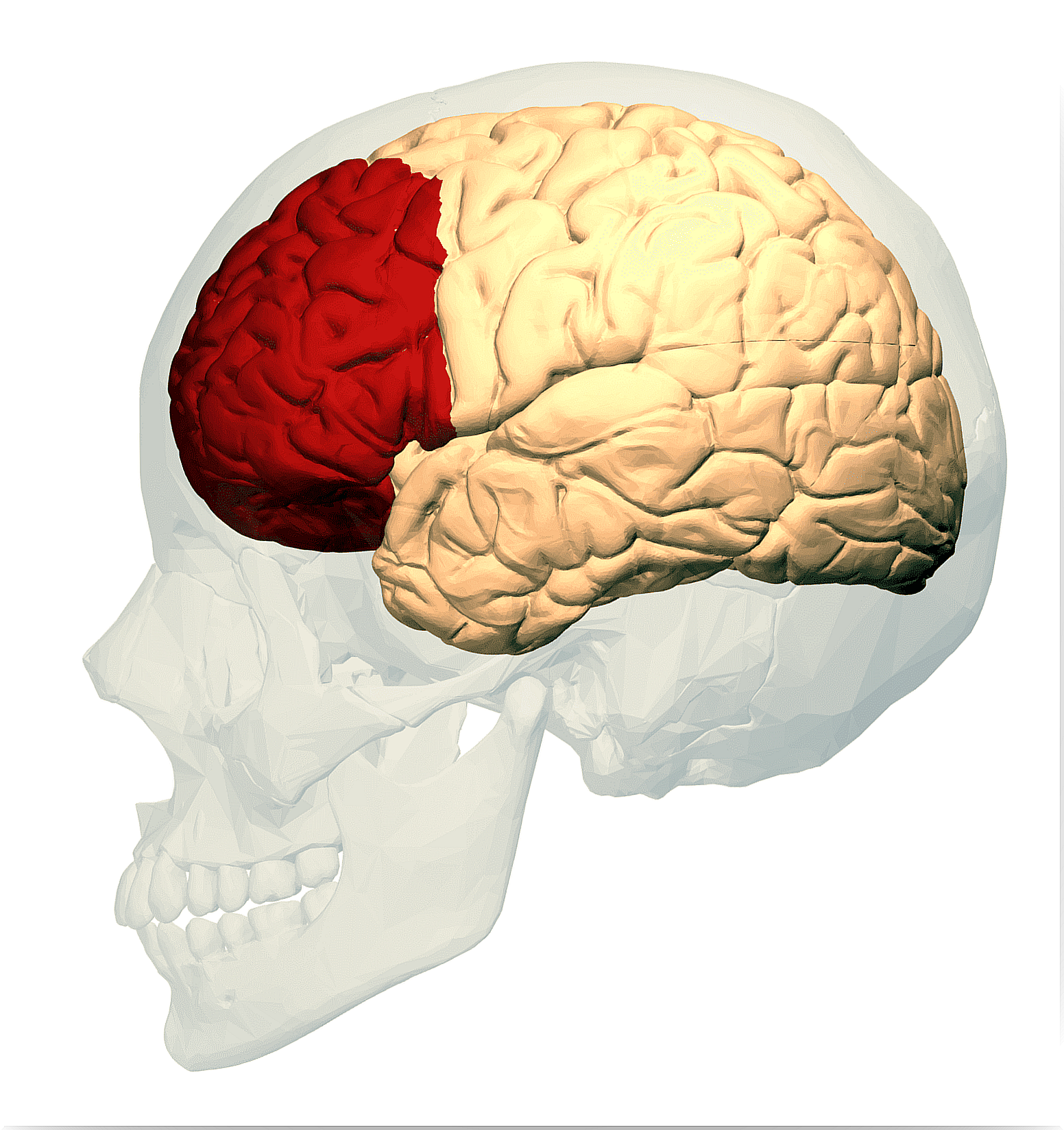
Anatomy of the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is divided into several areas:
- Motor, premotor and additional area
- Frontal eye field
- Broca area
- Prefrontal cortex
The latter is subdivided into three areas:
- Dorsolateral
- Orbital
- Medial
The main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Stuss and Knight (2002) as well as Tirapu and Ustárroz (2012) highlight some of the main characteristics of this cortex:
- Inhibition, coordination and modulation of behavior
- Search, retrieve and update relevant information at all times
- Planning, preparation and anticipation through time signals
- Cognitive and emotional regulation and control
- Flexibility to change attention and behavior as conditions change
For its part, Burguess’ team (2012) conducted a review of the scientific literature on the main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. They concluded that most researchers agreed that attention, memory, language, preparation and organization in the form of temporal sequences are the most important functions.
Attention, one of the essential functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Among the main functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is the control of attention. This control includes processes such as: task change, shared attention span, preparation for action, and interference control.
Memory
With regard to memory, we must distinguish between working memory or operative memory and declarative memory. Working memory is a system that allows information to be stored and used temporarily. Baddeley (2010) asserts that the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex acts as a “central executive”; according to the author, it has “ the capacity to recover information and to keep it active during its manipulation ”.
For their part, Stuss and Levine (2002) postulate that the participation of this region increases when the information requested “ exceeds the capacity of working memory and when it is necessary to control the distractors that may interfere with the relevant information. we work with ”.
When it comes to declarative memory, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex seems to be involved in information seeking processes. It participates in the choice of the best information coding strategies and deals with the processes associated with the memory of the source. That is to say, remembering the characteristics of an event: what, how, when, where …

Alterations in the memory of the source affect the ability of subjects to examine the origin of their memories. This process is known as reality monitoring. This way, they can distinguish real events from imaginary events. Baddeley assures “ that a deficit in this process may be responsible for the phenomena of proactive interference and the frequent intrusions and confabulations presented by patients with prefrontal lesions ”.
Tongue
The lack of verbal fluency is linked to prefrontal lesions, especially those on the left side. At the same time, the narrative speech would also be affected in terms of simplification and omission of grammatical forms when alterations appear in this region.
Preparation and time sequencing
Finally, time planning is a key ability to organize activities and manage on a daily basis. Research highlights the importance of frontal areas in planning. Arnedo, Bembibre and Triviño (2013) assert that the preparation and temporal sequencing are carried out “ by a constant updating of the information relating to the time required to perform an action and to keep it in memory until the moment of its execution. “.